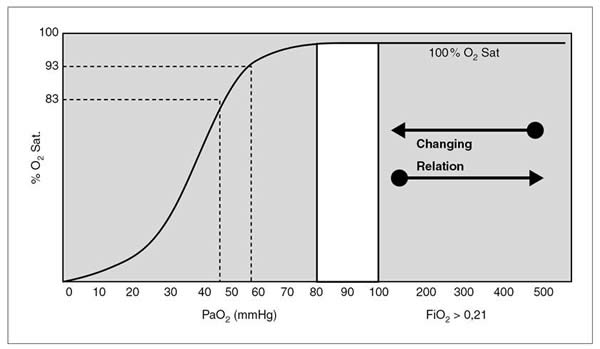
oxygen delivery devices and flow rates australia
Low-flow oxygen delivery systems deliver oxygen at flow rates below the patients inspiratory flow rate entrain room air and provide a variable FiO2. Dropping the oxygen flow rate closer to 10 Lmin-1 has been suggested as a compromise but the.
Saturations stable at 92 in a patient without lung disease Hudson mask rarely used Delivers 30-40 oxygen Flow rate 5-10Lmin Venturi mask Delivers 24-60 oxygen.
. The measured and set flow rates of both stationary and portable canisters were strongly correlated. However when breathing with the NRB an O 2 flow rate of 15 Lmin-1 is required to reach these levels. The recommended initial oxygen flow rate for open-circuit systems employing a non-rebreather mask has long been 15 Lmin-1.
They deliver oxygen at flow rates below the patients respiratory requirements. A higher FiO2 can be achieved with flow rates up to 6 Lmin if tolerated. Oxygen can be administered at 6 liters per minute or less and flow rates of 4 liters per minute or less.
Blake DF Crowe M Lindsay D Brouff A Mitchell SJ Pollock NW. MORS with an oronasal or intraoral mask demand valve with an intraoral mask and NRB at a flow rate of 15 Lmin¹. For simple face masks flow rates of.
However there is a small amount of room air which gets in the system so the FIO2 is invariably lower more like 80-90. Adapters deliver set amounts of FiO2 at 24 to 60. Comparison of tissue oxygenation achieved breathing oxygen from a demand valve with four different mask configurations.
For example patients commonly use a flow rate of 2 liters per minute but the flow rate varies by each patients needs. 200969111 Bailey P Thomsen GE Spuhler VJ et alCrit Care MedJan2007351139145. Low flow systems such as oxygen concentrators generate flow rates of 5-10 litresm.
You decided to shift to simple mask a flow rate of 15 to 60 lminute low flow device most common device used for mild hypoxia can be set between 1 and 6 lpm 24 to 40 fio2 fio2 increases approximately 4 with each liter of o2 korupolur gj needham dmcontemporary criticalcare. Can delivery precise and dependable FiO2. The various modes of oxygen administration include an intubation tube nasal cannula oxygen mask reservoir face mask venturi mask and high-flow nasal cannula HFNC The fraction of inspired oxygen FiO 2 represents the.
Looping the tubing around the patients ears and bring it to the front of the patients chest. Stationary and portable 9 10. Types of oxygen concentrators and oxygen delivery There are two types of oxygen concentrators.
If oximetry is not available or reliable oxygen saturations cannot be determined and hypoxaemia is suspected oxygen can be delivered at. NASAL CANNULAE oxygen delivery device NASAL CANNULAE ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES. 6 rows Device.
Given typical supply limitations there is a natural interest in reducing the flow rate to extend oxygen delivery duration. Oxygen administration performed in both acute and chronic phases of respiratory failure is a common procedure in clinical medicine. A typical oxygen concentrator may deliver oxygen flows of 055 Lmin 1 low-flow oxygen concentrators while some models may generate up to 10 Lmin 1 high-flow oxygen concentrators 9 10.
2 to 15 Lmin. Oxygen delivery devices and flow rates should be adjusted to keep the oxygen saturation in the target range. Nasal cannulae-delivering low flow rates of 24 Lmin or more are provided to patients almost automatically in a range of common clinical situations without the oxygen even necessarily being.
1-2 Lmin via nasal cannulae or 2-4 Lmin via 24 or 28 Venturi mask in patients with acute exacerbations of COPD or conditions known to. Expressed as a percentage of the set flow rate the measured flow rate of the canisters varied from 36-128 with the lowest values at flow rates flow rates differed or 10 from the set flow rate. They can deliver between 2435 oxygen with flow rates of 24 Lmin.
Of the commonly available devices promoted for O₂ delivery to injured divers similar PtcO₂ and nasopharyngeal F I O₂ values were obtained with the three devices tested. 2435 FiO2 at a flow of 14. Connect the face mask to the oxygen cylinder.
A comparison of the tissue oxygenation achieved using different oxygen delivery devices and flow rates. Apply the nasal cannula to the patients nose first. The advantages and disadvantages of nasal cannulae are summarised below.
If the nasal prongs are curved these should face posteriorly to the patient. Only goes up to 60 FIo2 so not for patients who have significantly high oxygen demands bulky. Set flow rate at 1 to 4 litres per minute.
Peak nasopharyngeal F I O 2 was highest with the NRB with a flow rate of 15 Lmin-1 Table 3 though 10-min P tc O 2 values were similar for each device. Oxygen Delivery Systems LOW FLOW OXYGEN DEVICES HIGH FLOW OXYGEN DEVICES Cannot deliver constant FiO 2 Maintain constant FiO 2 Flow 6 - 8 Lmin Delivering O 2 at very high flow Mixture of oxygen room air Flow usually 4 times the actual Minute volume FiO 2 varies with tidal volume-Shallow breathing less entrainment of room air high FiO 2. Deliver 24-30 oxygen Flow rate 1-4Lmin 4L will dry the nose 2L is more comfortable Used in non-acute situations or if only mildly hypoxic eg.
Low flow device Most common device used for mild hypoxia Can be set between 1 and 6 LPM 24 to 40 FiO2 FiO2 increases approximately 4 with each liter of O2 KorupoluR GJ Needham DMContemporary CriticalCare.

Transtracheal Catheter Image Courtesy Www Airwayeduca Download Scientific Diagram
Clinical Guidelines Nursing Oxygen Delivery
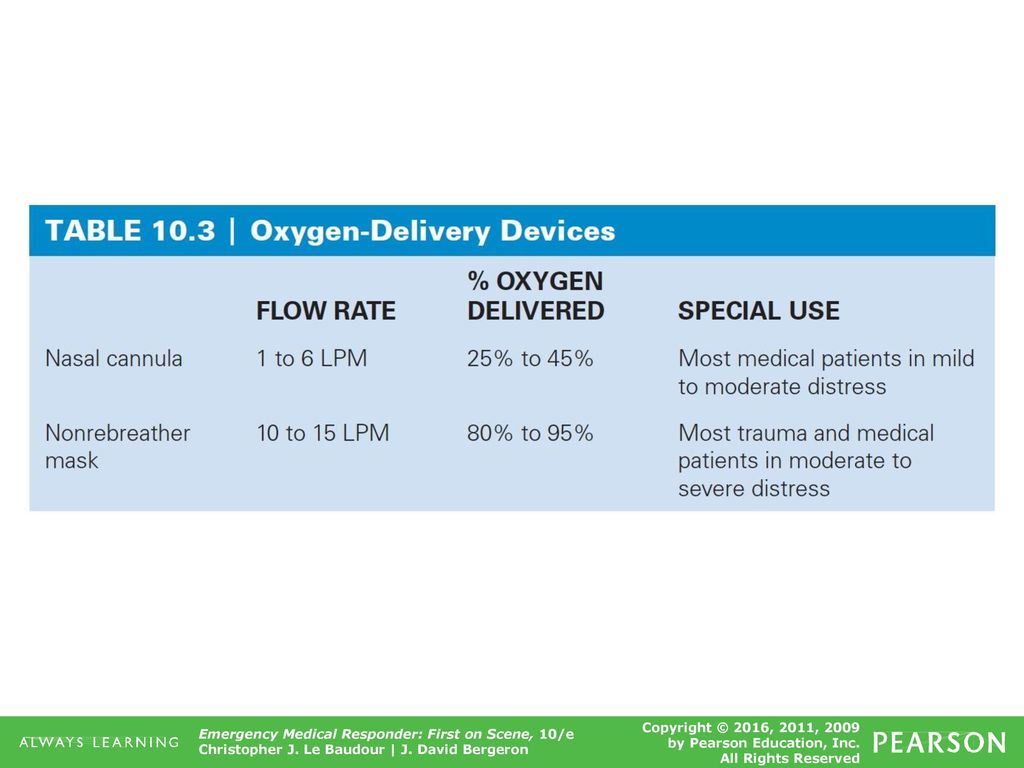
10 Principles Of Oxygen Therapy Ppt Download

Nursing Jobs Are Noble Profession Especially In Aboard You Can Earn More In Aboard On Nursing Professions Emergency Nursing Nursing Jobs Nursing Profession

Thoracic Society Of Australia And New Zealand Position Statement On Acute Oxygen Use In Adults Swimming Between The Flags Barnett 2022 Respirology Wiley Online Library
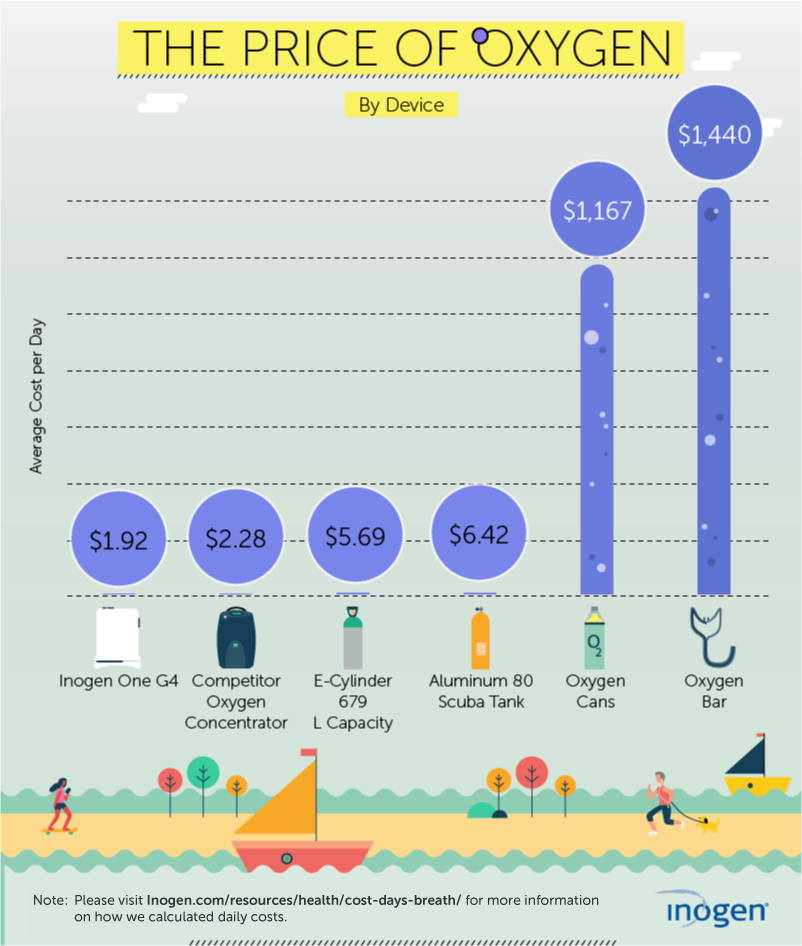
Cost Of Oxygen Portable Oxygen Concentrator Cost Inogen
Clinical Guidelines Nursing Oxygen Delivery

O Two Single Use Cpap Otwo Com

Initial Or Starting Flows Of High Flow Nasal Cannula In A Pediatric Download Table
Automatic Oxygen Titration Versus Constant Oxygen Flow Rates During Walking In Copd A Randomised Controlled Double Blind Crossover Trial Thorax

Automatic Oxygen Titration Versus Constant Oxygen Flow Rates During Walking In Copd A Randomised Controlled Double Blind Crossover Trial Thorax

Transtracheal Catheter Image Courtesy Www Airwayeduca Download Scientific Diagram